Unprintable - Hack The Box Challenge
Image:
Description:
We found this image in a box in space. It seems like extraterrestrial civilisations left it for us to find. Can you crack their code?
This is one of the two most difficult challenges for stego on this website and with good reason.
Let’s start
Converting the image into a binary string
We can see that the image is formed by black and white squares so at the beginning I tought each pixel would represent each square but it seems each square is 10 pixels. So I was processing it every 10.
def generate_binary_string():
try:
img = Image.open("Unprintable.png") # Open the img
except:
print('Put Unprintable.png file on this directory')
exit(1)
pixels = img.convert('RGB') #Convert it in RGB
width, height = img.size #Getting the img's dimension
binary_string = ""
#Loop every 10 pixels
for y in range(0, height, 10):
for x in range(0, width, 10):
r, g, b = pixels.getpixel((x, y))
if r == g == b == 0: #If the pixel is 0 = black = 0
binary_string += "0"
elif r == g == b == 255: #If the pixel is 255 = white = 1
binary_string += "1"
return binary_string
The output would be:
00101101010110110011011100101101001111100010101100111100010111010011111000101101001011101000100001011...
Decode the binary string (Conversion into ASCII)
We’ll need first of all convert the binary string in bytes (each 8 bits what will represents a ASCII char)
def bitstring_to_bytes(s):
v = int(s, 2)
b = bytearray()
while v:
b.append(v & 0xff)
v >>= 8
return bytes(b[::-1])
And then just decode each byte..
Doing that I found problems to decode certain bytes… I’ll show you the raw output from convert each byte into a ASCII char:
The raw output:
-[7->+<]>-.\x88[3\x83+\x86>-.[5\x83+\x86>2-.4\x80\x832+\x86\x8.\x80\x8e5+\x90>+.\x802\x8e+\x86\x88.[5\x83+\x90>3-.3+.2+..
The problem is that \x88 or \x86, so searching in internet, this post gaves me the solution.
It’s RLE enconded brainfuck and the bytes in between are compression, so to decompress we have to take the byte, \x88 and get the 8º char of the string with the next char to replace it so the result would be
>-.
There’s another case, another byte we don’t want is +1, so if \x9e would decode to \x88 and \x88 +1 it only decodes to \x88 wich would be again >-.
To resolve them, you take the byte at string[index] and string[index+1], then replace the unprintable byte with those two characters.
The func:
def get_replace(binary_values,bs,next=False):
index = int.from_bytes(bs, "little") - 128
if(next):
_bs = bitstring_to_bytes(binary_values[index + 1])
else:
_bs = bitstring_to_bytes(binary_values[index])
return _bs
def decode_binary(binary_string):
binary_values = [binary_string[i:i+8] for i in range(0, len(binary_string), 8)]
decoded_str = ""
raw_str=""
for i in range(len(binary_values)):
bs = bitstring_to_bytes(binary_values[i])
raw_str += str(bs).replace("b'","").replace("'","")
try:
decoded_str += bs.decode()
except:
_bs = get_replace(binary_values,bs)
try:
decoded_str += _bs.decode()
except:
__bs = get_replace(binary_values, _bs)
decoded_str += __bs.decode()
__bs = get_replace(binary_values, _bs, True)
decoded_str += __bs.decode()
continue
_bs = get_replace(binary_values, bs, True)
try:
decoded_str += _bs.decode()
except:
__bs = get_replace(binary_values, _bs)
decoded_str += __bs.decode()
__bs = get_replace(binary_values, _bs, True)
decoded_str += __bs.decode()
print("\033[94m" + "The raw decoded string is:\n" + '\033[1;37;0m' + raw_str )
return decoded_str
So the correct output is like:
-[7->+<]>-.>-[3->+<]>-.[5->+<]>2-.4-[->2+<]>-.-[->5+<]>+.-[2->+<]>-.[5->+<]>3-.3+.2+.>-[5->+<]>.2-[3->2+<]>3...
RLE Decode (Run Length Encoding Decode)
The decoding process it’s basicly find numbers which will indicate the number of repetitions of the next character.
An example is : 7- would be decoded as -------
So..
def rle_decode(decoded_str):
final_decoded_string = ""
i = 0
while i < len(decoded_str):
if decoded_str[i].isdigit():
if decoded_str[i + 1].isdigit():
final_decoded_string += int(decoded_str[i] + decoded_str[i + 1]) * decoded_str[i + 2]
i += 3
else:
final_decoded_string += int(decoded_str[i]) * decoded_str[i + 1]
i += 2
else:
final_decoded_string += decoded_str[i]
i += 1
return final_decoded_string
Unbrainfuck this
I just used the brainfuck module
Instalation:
pip install brainfuck-interpreter
Execution:
brainfuck.evaluate(final_decoded_string)
So the output of the script is:
Autopwn
# !/usr/bin/env python3
from PIL import Image
import brainfuck
def bitstring_to_bytes(s):
v = int(s, 2)
b = bytearray()
while v:
b.append(v & 0xff)
v >>= 8
return bytes(b[::-1])
def get_replace(binary_values,bs,next=False):
index = int.from_bytes(bs, "little") - 128
if(next):
_bs = bitstring_to_bytes(binary_values[index + 1])
else:
_bs = bitstring_to_bytes(binary_values[index])
return _bs
def generate_binary_string():
try:
img = Image.open("Unprintable.png") # Open the img
except:
print('Put Unprintable.png file on this directory')
exit(1)
pixels = img.convert('RGB') #Convert it in RGB
width, height = img.size #Getting the img's dimension
binary_string = ""
# Loop every 10 pixels
for y in range(0, height, 10):
for x in range(0, width, 10):
r, g, b = pixels.getpixel((x, y))
if r == g == b == 0: #If the pixel is 0 = black = 0
binary_string += "0"
elif r == g == b == 255: #If the pixel is 255 = white = 1
binary_string += "1"
return binary_string
def decode_binary(binary_string):
binary_values = [binary_string[i:i+8] for i in range(0, len(binary_string), 8)]
decoded_str = ""
raw_str=""
for i in range(len(binary_values)):
bs = bitstring_to_bytes(binary_values[i])
raw_str += str(bs).replace("b'","").replace("'","")
try:
decoded_str += bs.decode()
except:
_bs = get_replace(binary_values,bs)
try:
decoded_str += _bs.decode()
except:
__bs = get_replace(binary_values, _bs)
decoded_str += __bs.decode()
__bs = get_replace(binary_values, _bs, True)
decoded_str += __bs.decode()
continue
_bs = get_replace(binary_values, bs, True)
try:
decoded_str += _bs.decode()
except:
__bs = get_replace(binary_values, _bs)
decoded_str += __bs.decode()
__bs = get_replace(binary_values, _bs, True)
decoded_str += __bs.decode()
print("\033[94m" + "The raw decoded string is:\n" + '\033[1;37;0m' + raw_str )
return decoded_str
def rle_decode(decoded_str):
final_decoded_string = ""
i = 0
while i < len(decoded_str):
if decoded_str[i].isdigit():
if decoded_str[i + 1].isdigit():
final_decoded_string += int(decoded_str[i] + decoded_str[i + 1]) * decoded_str[i + 2]
i += 3
else:
final_decoded_string += int(decoded_str[i]) * decoded_str[i + 1]
i += 2
else:
final_decoded_string += decoded_str[i]
i += 1
return final_decoded_string
if __name__ == "__main__":
binary_string = generate_binary_string()
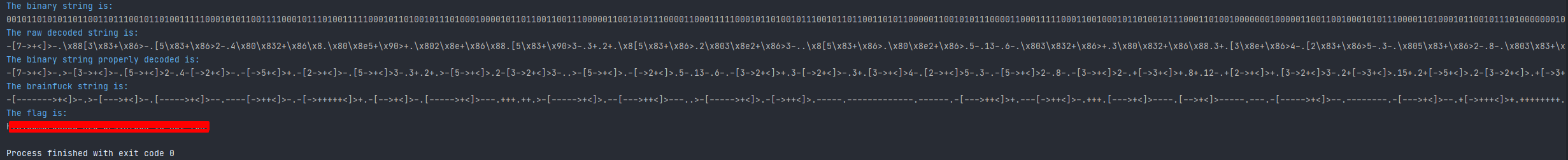
print("\033[94m" + "The binary string is:\n" + '\033[1;37;0m' + binary_string)
decode_binary = decode_binary(binary_string)
print("\033[94m" + "The binary string properly decoded is: \n" + '\033[1;37;0m' + decode_binary)
final_decoded_string = rle_decode(decode_binary)
print("\033[94m" + "The brainfuck string is: \n" + '\033[1;37;0m' + final_decoded_string)
flag = brainfuck.evaluate(final_decoded_string)
print("\033[94m" + "The flag is:\n" + '\033[1;37;0m' + flag)
Byee

 Hack The Box
Hack The Box
 Try Hack Me
Try Hack Me